A Crash Course on the Many Types of Sugar
All sugar is made by first extracting sugar juice from sugar beet or sugar cane plants., and from there, many types of sugar can be produced.
Learn MoreSugar is naturally white. When the sugar is initially extracted from the plants, it has a golden color because of the non-sugar materials attached to and within the sugar crystals. This golden sugar is then purified, where these plant fibers and molasses are removed, extracting the sugar molecules from the non-sugar materials and restoring the sugar crystals to their natural white color.
Most of the non-sugar materials generated in sugar processing are used for other purposes, recycled or reused.
 Molasses, used by feed companies, bakers, distillers and pharmaceutical companies, for animal feed and many more products, is extracted through the beet and cane sugar refining processes. It takes about four rounds of extraction to remove the molasses to obtain the maximum amount of sucrose.
Molasses, used by feed companies, bakers, distillers and pharmaceutical companies, for animal feed and many more products, is extracted through the beet and cane sugar refining processes. It takes about four rounds of extraction to remove the molasses to obtain the maximum amount of sucrose.
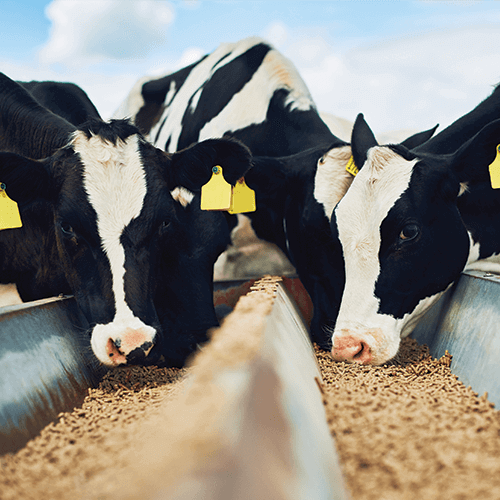 The sugar beet residue, or pulp, is generally used for animal feed or further processed for use as other carbohydrate-based products.
The sugar beet residue, or pulp, is generally used for animal feed or further processed for use as other carbohydrate-based products.
 The sugar cane stalk residue, called bagasse, is often used as fuel to run the cane factory. Many sugar cane mills and refineries produce their own electricity, and some even supply power to nearby towns.
The sugar cane stalk residue, called bagasse, is often used as fuel to run the cane factory. Many sugar cane mills and refineries produce their own electricity, and some even supply power to nearby towns.
 In addition, much of the water removed along the way still contains sucrose (called “sweetwater”), so it’s pumped back into the stations to be used again.
In addition, much of the water removed along the way still contains sucrose (called “sweetwater”), so it’s pumped back into the stations to be used again.
 Carbon used in sugar cane filtration is recharged (revivified) and reused too.
Carbon used in sugar cane filtration is recharged (revivified) and reused too.
All sugar is made by first extracting sugar juice from sugar beet or sugar cane plants., and from there, many types of sugar can be produced.
Learn MoreHere are some quick definitions and links to what these terms actually mean.
Learn More© 2026 The Sugar Association, Inc. All rights reserved.
Get Social with #MoreToSugar